This machine will perform the attack.
nano grab.py
In nano, enter this code, as shown below:
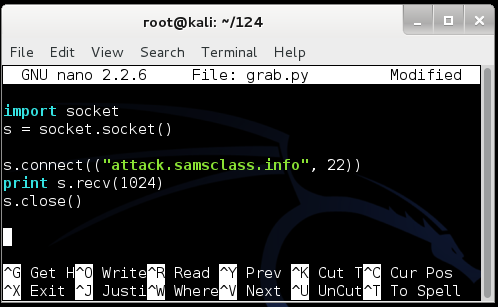
import socket
s = socket.socket()
s.connect(("attack.samsclass.info", 22))
print s.recv(1024)
s.close()
Save the file with Ctrl+X, Y, Enter.
Explanation
The first line imports the "socket" library, which contains networking functions.The second line creates a socket object named "s".
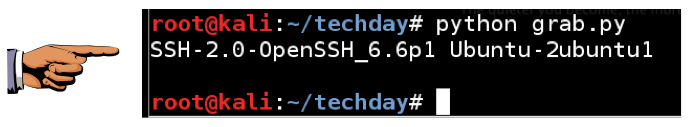
The third line connects to the server "attack.samsclass.info" on port 22.
The fourth line receives data from the server and prints it, up to a maximum of 1024 characters.
The fifth line closes the connection.
python grab.py

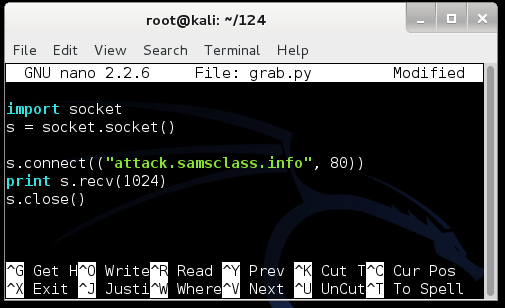
Change the port number from 22 to 80, as shown below, and save the modified file.
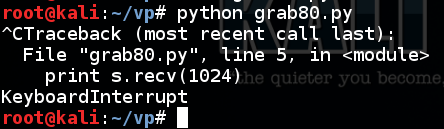
Run the script again. There is no banner from an HTTP server, so it just freezes up, waiting for a banner. To stop the script, press Ctrl+C.
To make it timeout more quickly, add this line to your script, as shown below:
socket.setdefaulttimeout(2)
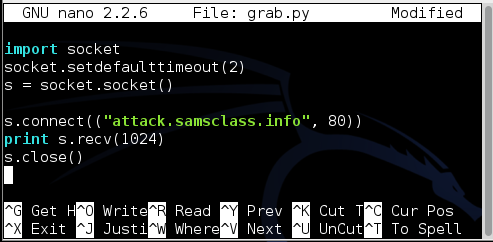
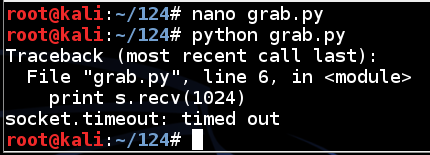
Run the script again. Now it times out, as shown below.
cp grab.py grab2.py
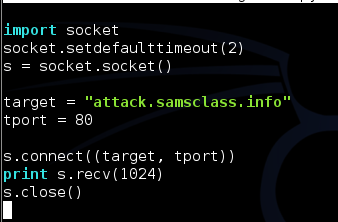
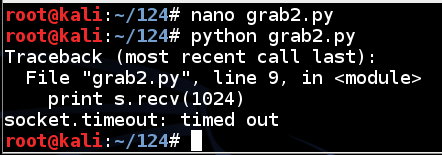
Save and run the script--it should time out in a few seconds, just as it did before.
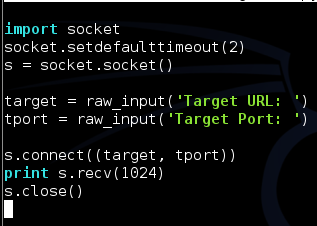
Save and run the script. Enter a URL and port to scan. The script halts with an error saying "TypeError: an integer is required".
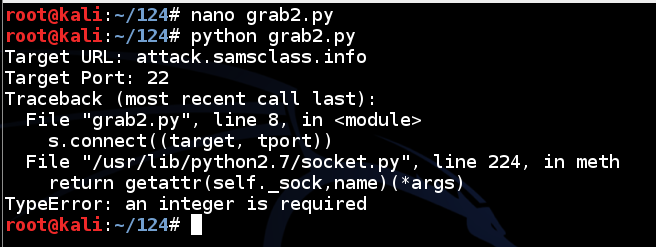
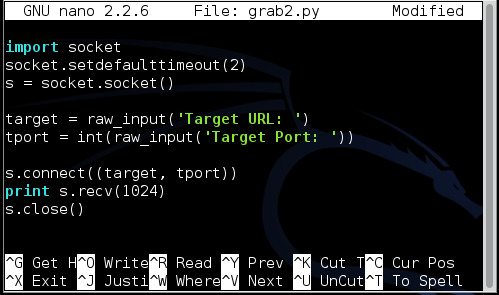
To fix that, enclose the raw_input statement for tport in the int() function, as shown below.
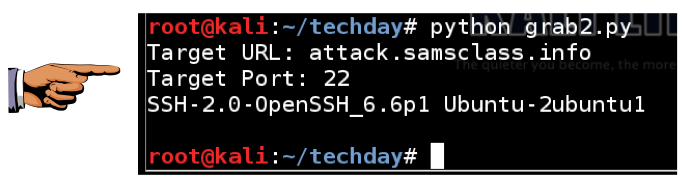
Now the port scanner works. Use it to grab the port 22 banner again, as shown below.
Last updated 6-16-16