Windows or Other Intel-Based Systems
For Windows or other systems with Intel processors, such as older Macs.If you are using VMware
- Download this file:
- Ub20.04_w_ARM.vmwarevm.zip
- File size: 2,868,410,883 bytes (2.87 GB)
- SHA256(Ub20.04_w_ARM.vmwarevm.zip)= f609ac67460be33bfe84b41acffd4a6c9b117212e66c096f482609b890bd6251
- Root password (you don't really need it): P@ssw0rd
- Unzip the file. Double-click the .VMX file inside to launch the VM in VMware.
- Log in with a username of student and a password of P@ssw0rd
If you are using VirtualBox
- Download this file:
- Ub20.04_w_ARM_OVF.zip
- File size: 4,290,791,832 bytes (4.3 GB)
- SHA256(Ub20.04_w_ARM_OVF.zip)= 9f77d4e752c96d2783158dab8c4757df2daa866fed7972edb1692511c857fe2b
- Root password (you don't really need it): P@ssw0rd
- Unzip the file. Import the .ovf file inside to launch the VM in VirtualBox.
- Log in with a username of student and a password of P@ssw0rd
Mac M1 or Other ARM64-Based Systems
For the Mac M1, using 64-bit ARM:
- Download this file:
- Ub22_wARM32_M1.zip
- File size: 2,584,390,888 bytes (2.6 GB)
- SHA256(Ub22_wARM32_M1.zip)= d75b38fd9a96b51f5270340ab2a3e1480bd8c61af6e8b55589b6cb325d8c4454
- Unzip the file.
- In Finder, double-click the .vmwarewvm file inside to launch the VM in VMware.
- In VM settings, disconnect the CD-ROM and restart the VM
- Log in with a username of student and a password of P@ssw0rd
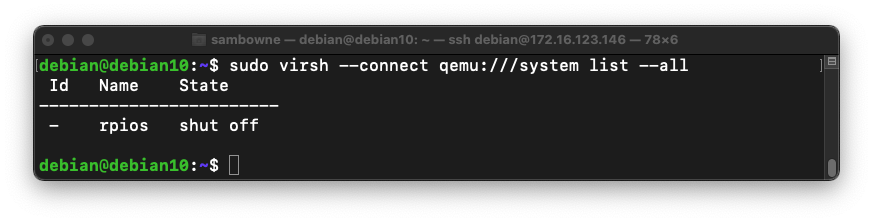
sudo virsh --connect qemu:///system list --all
You should see a machine named "rpios" with a State of "shut off", as shown below.

From the Ubuntu host system, at the student@ubuntu20:~$ prompt, execute this command to start the ARM32 VM:
sudo virsh --connect qemu:///system start rpios --console
Notice the IP address of your ARM32 machine, shown in the first line of the image below.
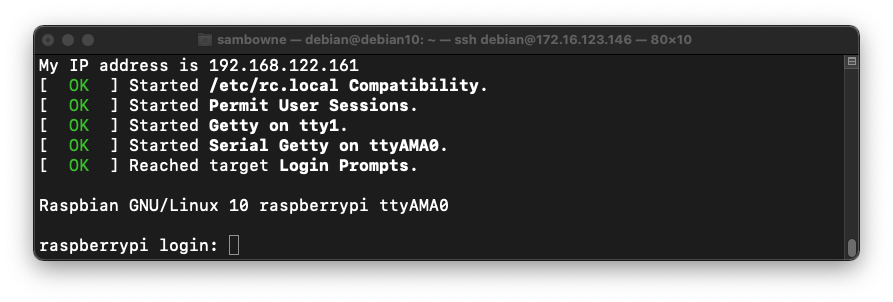
Log in with a username of pi and a password of raspberry
ED 41.1: OS Version (10 pts)
In the ARM virtual machine, execute this command:The flag is covered by a green rectangle in the image below.
From inside the ARM32 VM, at the pi@raspberrypi:~$ prompt, execute this command:
sudo poweroff
sudo virsh --connect qemu:///system reset rpios
sudo virsh --connect qemu:///system list --all
cd
sudo ./start_arm64.sh
The ARM64 OS starts, ending with a login prompt, as shown below.
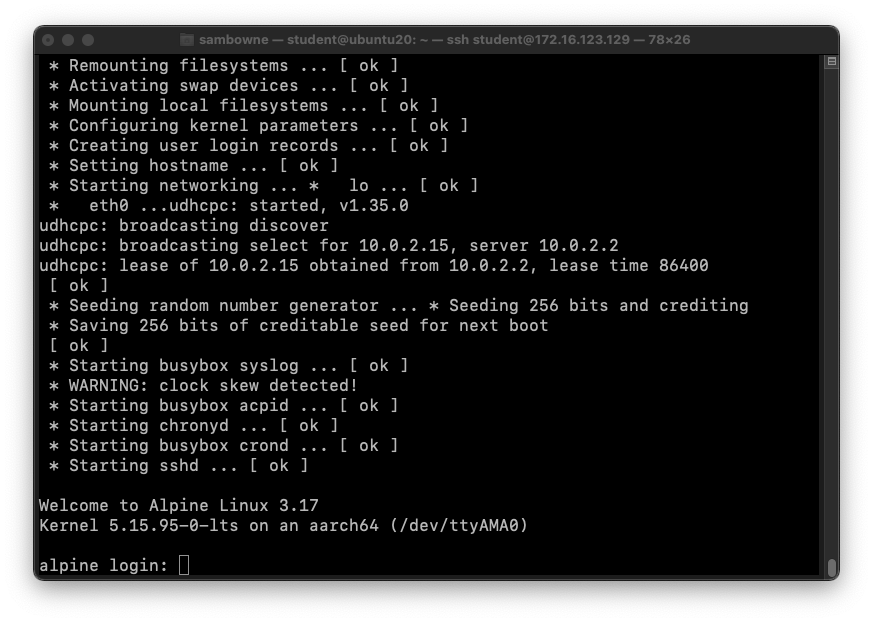
In the ARM64 VM, at the "alpine login:" prompt, log in with a username of student and a password of P@ssw0rd
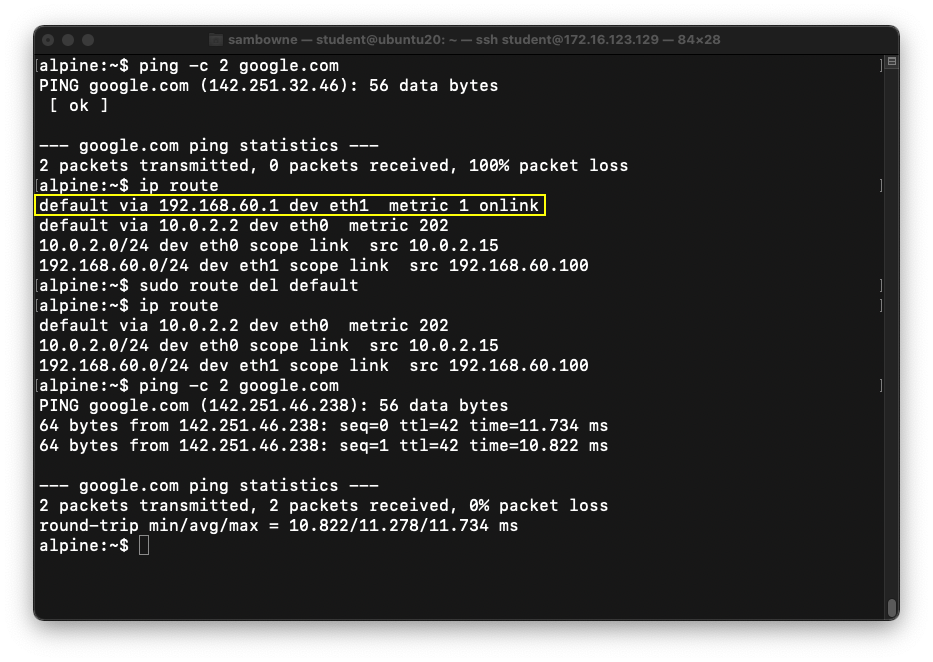
In the ARM64 VM, at the alpine:~$ prompt, execute these commands, one at a time, to fix a networking problem.
If you are prompted to enter a password, enter a password of P@ssw0rd
ping -c 2 google.com
ip route
sudo route del default
ip route
ping -c 2 google.com
ED 41.2: OS Version (5 pts)
In the ARM64 VM, at the alpine:~$ prompt, execute this command:The flag is covered by a green rectangle in the image below.
sudo poweroff
Making an OVF for VirtualBox from a VMware Machine
There's no need to do this--I already did it. I'm only putting this here to help me remember how I did it for future reference.On a Mac with VMware Fusion installed, this command converts a VMware VM to an OVF:
The result is three files:
Ub20.04_w_ARM.mf
Ub20.04_w_ARM.ovf
Posted 2-23-23
M1 file changed 3-1-23
ovftool instructions added 7-20-23